MySQLProxySQL基于MGR的读写分离
之前已经跟大家介绍过了通过MYSQLSHELL部署MGR
MySQL-通过mysql-shell部署MGR
再简单的介绍一下MGR的功能:
- mysql原生的高可用方案
- 支持自动故障自愈
- 支持自动差异数据补偿
- 支持通过clone的方式快速拉起一个新节点
根据上文,我们已经部署出一套一主二从的MGR,现在需要通过ProxySQL配合MGR实现读写分离。
同样,本文主要介绍ProxySQL配合MGR做读写分离的部署流程,关于实现原理将在后文介绍。
部署流程
1、通过mysql-shell部署mgr
略
192.168.14.11:3306 master
192.168.14.12:3306 slave
192.168.14.13:3306 slave
2、部署proxysql
#下载地址
https://repo.proxysql.com
#rpm安装自带依赖
yum install -y proxysql-2.0.10-1-centos7.x86_64.rpm
验证proxysql是否安装成功
端口监听6033、6032
登录proxysql管理端
mysql -uadmin -padmin -h127.0.0.1 -P6032
3、创建proxysql监控用户和业务用户,并赋予权限(MGR-master)
create user proxysql_monitor@’%’ identified with mysql_native_password by ‘123456’;
grant all ON . to proxysql_monitor@’%’;
create user test_work@’%’ identified with mysql_native_password by ‘123456’;
grant all ON . to test_work@’%’;
flush privileges;
4、注册监控用户(ProxySQL)
set mysql-monitor_username=‘proxysql_monitor’;
set mysql-monitor_password=‘123456’;
load mysql variables to runtime;
save mysql variables to disk;
5、配置主从分组信息(ProxySQL)
insert into mysql_group_replication_hostgroups values (10,20,30,40,1,1,0,‘100’,‘proxysql’);
load mysql servers to runtime;
save mysql servers to disk;
mysql_group_replication_hostgroups详解
write_hostgroup:
默认情况下会将所有流量发送到这个组。具有read_only=0的节点也将分配到这个组;
backup_writer_hostgroup:
如果集群有多个写节点(read_only=0)且超过了max_writers规定数量,则会把多出来的写节点放到备用写组里面;
reader_hostgroup:
读取的流量应该发送到该组,只读节点(read_only=1)会被分配到该组;
offline_hostgroup:
当ProxySQL监视到某个节点不正常时,会被放入该组;
active:
是否启用主机组,当启用时,ProxySQL将监视主机在各族之间移动;
max_writers:
最大写节点的数量,超过该值的节点应该被放入backup_write_hostgroup;
writer_is_also_reader:
0:写节点只能写,读节点只能读
1:写节点能读写,读节点只能读
2:写节点能读写,另一个备用写节点只能读,其他节点,不能读写

6、创建视图(MGR-master)
USE sys;
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS gr_member_routing_candidate_status;
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS IFZERO;
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS LOCATE2;
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS GTID_NORMALIZE;
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS GTID_COUNT;
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS gr_applier_queue_length;
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS gr_member_in_primary_partition;
DROP FUNCTION IF EXISTS gr_transactions_to_cert;
DELIMITER $$
CREATE FUNCTION IFZERO(a INT, b INT)
RETURNS INT
DETERMINISTIC
RETURN IF(a = 0, b, a)$$
CREATE FUNCTION LOCATE2(needle TEXT(10000), haystack TEXT(10000), offset INT)
RETURNS INT
DETERMINISTIC
RETURN IFZERO(LOCATE(needle, haystack, offset), LENGTH(haystack) + 1)$$
CREATE FUNCTION GTID_NORMALIZE(g TEXT(10000))
RETURNS TEXT(10000)
DETERMINISTIC
RETURN GTID_SUBTRACT(g, '')$$
CREATE FUNCTION GTID_COUNT(gtid_set TEXT(10000))
RETURNS INT
DETERMINISTIC
BEGIN
DECLARE result BIGINT DEFAULT 0;
DECLARE colon_pos INT;
DECLARE next_dash_pos INT;
DECLARE next_colon_pos INT;
DECLARE next_comma_pos INT;
SET gtid_set = GTID_NORMALIZE(gtid_set);
SET colon_pos = LOCATE2(':', gtid_set, 1);
WHILE colon_pos != LENGTH(gtid_set) + 1 DO
SET next_dash_pos = LOCATE2('-', gtid_set, colon_pos + 1);
SET next_colon_pos = LOCATE2(':', gtid_set, colon_pos + 1);
SET next_comma_pos = LOCATE2(',', gtid_set, colon_pos + 1);
IF next_dash_pos < next_colon_pos AND next_dash_pos = ((SELECT
COUNT(*)
FROM
performance_schema.replication_group_members) / 2) = 0),
'YES',
'NO')
FROM
performance_schema.replication_group_members
JOIN
performance_schema.replication_group_member_stats rgms USING (member_id)
WHERE
rgms.MEMBER_ID = my_server_uuid()),
'NO') AS viable_candidate,
IF((SELECT
((SELECT
GROUP_CONCAT(performance_schema.global_variables.VARIABLE_VALUE
SEPARATOR ',')
FROM
performance_schema.global_variables
WHERE
(performance_schema.global_variables.VARIABLE_NAME IN ('read_only' , 'super_read_only'))) 'OFF,OFF')
),
'YES',
'NO') AS read_only,
IFNULL(sys.gr_applier_queue_length(), 0) AS transactions_behind,
IFNULL(sys.gr_transactions_to_cert(), 0) AS transactions_to_cert;$$
DELIMITER ;
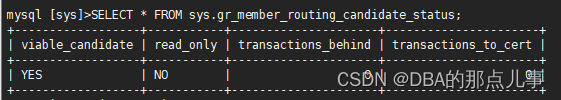
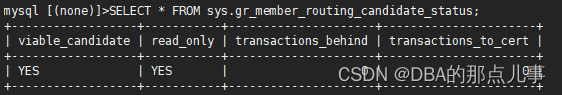
SELECT * FROM sys.gr_member_routing_candidate_status;
(master)
(slave)
7、添加服务器列表(ProxySQL)
insert into mysql_servers(hostgroup_id,hostname,port,weight,comment) values(10,‘192.168.14.11’,3306,1,‘mgr1’),(10,‘192.168.14.12’,3306,1,‘mgr2’),(10,‘192.168.14.13’,3306,1,‘mgr3’);
load mysql servers to runtime;
save mysql servers to disk;
mysql_servers具体说明
hostgroup_id:
ProxySQL经过hostgroup的形式组织后端db实例,一个hostgroup表明同属于一个角色,默认为0
hostname:
后端实例IP
port:
后端实例监听端口,默认为3306
status:
后端实例状态,默认为online,可取值为:
Ø online:当先后端实例状态正常
Ø shunned:临时被剔除,可能由于后端too many connections error,或者超过了可容忍延迟阀值max_replication_lag
Ø offline_soft:“软离线”状态,再也不接收新的链接,但已创建的链接会等待活跃事务完成
Ø offline_hard:“硬离线”状态,再也不接收新的链接,已创建的链接或被强制中断,当后端实例宕机或网络不可达时,会出现
weight:
后端实例权重,默认为1
max_connections:
容许链接到该后端实例的最大链接数,不能大于MySQL设置的max_connections,若是后端实例hostname:port在多个hostgroup中,以较大者为准,而不是各自独立容许的最大链接数,默认为1000
max_replication_lag:
容许的最大延迟,master节点不受此影响,默认为0,若是>0,monitor模块监控主从延迟大于阀值时,会临时把它变为shunned
max_latency_ms:
mysql_ping响应时长,大于这个阀值会把它从链接池中剔除(即便是ONLINE状态),默认为0
comment:
备注
8、配置访问用户(ProxySQL)
insert into mysql_users(username,password,default_hostgroup) values(‘test_work’,‘123456’,10);
load mysql users to runtime;
save mysql users to disk;
9、配置路由规则,实现读写分离
insert into mysql_query_rules(active,match_pattern,destination_hostgroup,apply) values(1,’^select.*for update$’,10,1),(1,’^select’,30,1);
load mysql query rules to runtime;
save mysql query rules to disk;
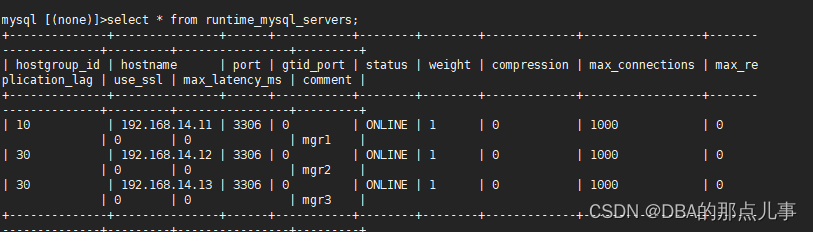
10、验证(ProxySQL)
select * from runtime_mysql_servers;
11、验证读写分离
读:
mysql -utest_work -p123456 -P6033 -h 127.0.0.1 -e “select@@server_id;”
写:
mysql -utest_work -p123456 -P6033 -h 127.0.0.1 -e “begin;select@@server_id;commit”;
测试故障自愈
MGR-master宕机
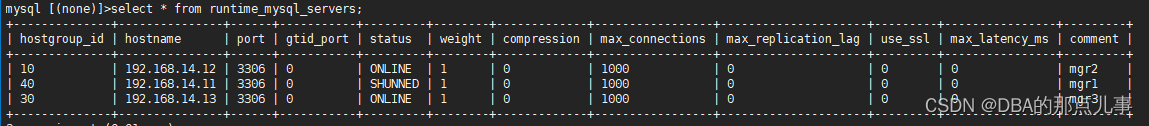
1、查看ProxySQL状态(ProxySQL)
select * from runtime_mysql_servers;
2、查看MGR状态(MGR)
select * from performance_schema.replication_group_members;
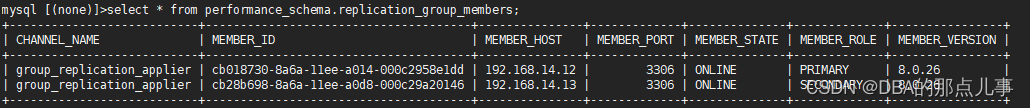
可以看到,master宕机后,MGR自动切换了主从关系,同时proxysql也自动切换的读写节点
MGR-宕机节点恢复
3、查看ProxySQL状态(ProxySQL)
select * from runtime_mysql_servers;
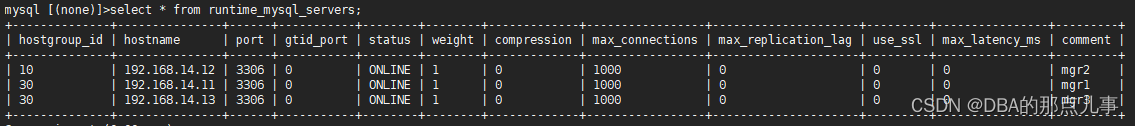
4、查看MGR状态(MGR)
select * from performance_schema.replication_group_members;
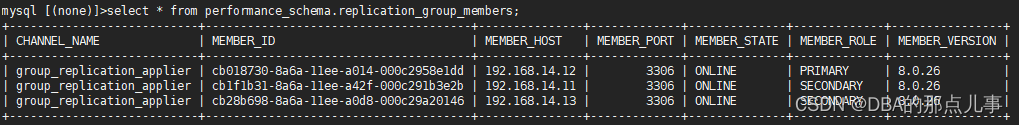
可以看到,宕机节点恢复后,自动回到MGR集群,同时在proxysql中也自动变成了读节点
彩蛋
当使用主从架构时,则在mysql_replication_hostgroups中配置分组信息(本文使用MGR模式,所以在mysql_group_replication_hostgroups中配置),同时不需要在MGR创建视图。
实则: 使用MGR时也可以用mysql_replication_hostgroups配置,不需要配置视图,其读写效果相当于mysql_group_replication_hostgroups的writer_is_also_reader配置为1
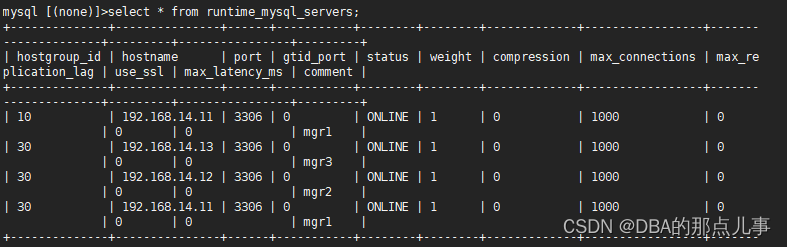 可以看到,写节点即可写又可读,其他节点只可读。
可以看到,写节点即可写又可读,其他节点只可读。
这种效果其实就是为了当所有读节点都挂完以后,剩下的唯一一个主节点依旧可以提供读写服务,相当于变成了一个单实例的mysql。





